Charging Standard For Phone & EV
1. Introduction
In the field of charging, the evolution of technology and the development of standards have been key factors driving the development of the industry. From the initial simple charging method to today’s complex charging ecosystem, we have witnessed rapid progress in charging technology. This process not only involves charging mobile devices and electric vehicles, but also includes multiple scenarios such as homes, industries and public places.
The development of charging industry standards and safety regulations is essential to ensure the safety, efficiency and interoperability of the charging process. This not only helps to protect the security of user devices, but also provides the basis for different devices and systems to work together. As technology continues to advance, new charging standards continue to emerge to adapt to changing market demands and technical challenges.
In this environment full of innovation and competition, this article will delve into the current status of charging industry standards and safety regulations, and explore the impact of various technological trends on the future charging industry. Through a comprehensive understanding of charging technology, we can better grasp the dynamics of the current industry and provide useful thinking for the construction of the future charging ecosystem. As we explore together, we will have a deeper understanding of the cutting-edge development of the charging industry.
2. Standard
2.1 Mobile Phone Fast Charge Standard (Public)
(1) USB PD
Full name: USB Power Delivery, a wired fast charge standard customized, modified and released by the USB-IF Association, is currently the most versatile and most likely to become a unified charging standard in the market.

PD fast charge protocol since the launch of PD 1.0 in 2012, after several generations of version updates, has been updated to the latest version of PD 3.1, the protocol is divided into two parts, one is the Standard Power Range (SPR), There is also an Extended Power Range (EPR). USB PD 3.1 currently supports up to 240W fast charge, equipped with USB Type-C interface, the product ecology around PD 3.1 has been very perfect, build a complete chain from the product terminal to the chip, to the production terminal.
(2) QC
Full name, Qualcomm Quick Charge, released by Qualcomm, the market with Snapdragon processor mobile phones can use this charging technology.

QC Protocol The first generation of the protocol QC 1.0 was launched in 2013, and the latest version is the QC 5.0 fast charge protocol released in July 2020. QC 5.0 supports dual battery series and 20V voltage output, INOV algorithm is upgraded to 4.0, support 3.3V ~ 20V voltage fine-tuning, making Qualcomm QC charging protocol truly complete support USB-PD charging standards and characteristics. Support 100W+ super fast charge, charge 50% in 5 minutes, charging efficiency is 70% higher than QC4, the charging speed is once again pushed to more than 4 times that of QC4, officially entering the triple-digit power era. The charging speed has been comprehensively improved, the efficiency is higher than previous generations, and the heat output is lower.
(3) PE
Full name PumpExpress, published by Mediatek. Is one of the earliest charging protocols, due to the low processor occupancy of mobile phones, making this protocol difficult to popularize.

On November 23, 2018, Mediatek announced the latest generation of fast charging technology – Pump Express5.0(hereinafter referred to as PE5.0) at the fourth Shenzhen Intelligent Fast Charging and Wireless Charging Technology Seminar held in Big Bit, which attracted the attention of the industry. The operation principle of PE5.0 is to use the traditional switching charge+ half-pressure charge pump, that is, half-pressure is used in the CC range, and traditional charge is used in other areas. Its handshake protocol caters to the latest international fast charge standard USB PD3.0 PPS.
PE5.0 charging head output power range of 20~40W+, 3A Type-C data cable, more than 20 charging safety protection design.
In terms of charging efficiency, the charging efficiency of PE5.0 can reach 97%. In the case of a battery capacity of 4000mAh, the maximum charging current is 6A, which reaches 50% within 20 minutes of charging and 70% within 30 minutes of charging. The previous generation PE4.0 charging efficiency reached 93%, compared to the new generation PE5.0 improved by 4%.
2.2 Wireless charging standard
(1) AirFuel
AirFue RF is a wireless power specification that uses radio frequency (RF) to charge multiple devices simultaneously in a three-dimensional range, providing true mobility freedom.

AirFuel RF is a contactless power transmission technology that creates power areas where energy can be collected for use by devices. The new AirFuel RF standard opens the door to wireless power technology for many new markets and applications. Multiple devices in a range of applications can be powered simultaneously within a few feet of the power source without the need for precise placement and without the hassle of wires or maintaining batteries.
(2) Qi
Launched by WPC(Wireless Power Consortium, Chinese name “Wireless charging Alliance”) for smartphones and other portable mobile devices wireless fast charging standard, Chinese pronunciation qi (fourth tone).
Qi is an open universal standard that can be used with any Qi device, so consumers do not need to use separate chargers, cables and adapters, and can safely and easily conduct wireless charging in various places such as homes, offices, stations, and hotels. Products using Qi technology must undergo rigorous testing to ensure safety, interoperability and energy efficiency. The Qi 1.3.3 protocol, which is currently being widely used, supports a maximum charging power of 15W.

In recent years, will be released the latest standard Qi2, Qi2 upgrade, the use of a new Qi Logo. The most important is to join the MPP (Magnetic Power Profile Magnetic Power Segment) protocol, which includes MPP as a technology branch under Qi2. In addition, all certification specifications must integrate authentication. For manufacturers, the “transmit coil reference type” is no longer required
(3) PMA
Full name: Power Matters Alliance. It was initiated by Duracell Powermat, which is a joint venture between P&G and Powermat, a wireless charging technology company, and has a relatively excellent comprehensive strength. In addition, Powermat is a supporting member of the Alliance for Wireless Power(A4WP) standard. Already, AT&T, Google and Starbucks have joined the PMA Alliance (short for Power Matters Alliance).

The PMA Alliance is committed to creating wireless power standards for mobile phones and electronic devices that meet the standards of the IEEE Society, and has a leadership position in the field of wireless charging. Duracell Powermat has released a WiCC charging card based on the Power Matters Alliance standard. Larger than an SD card, the WiCC is embedded with components such as coils and electrodes for electromagnetic induction contactless charging. The card is thin and can be inserted next to existing smartphone batteries, making it easy for many portable devices to support contactless charging.
(4) NFC
In 2020, the NFC Forum published the new Wireless Charging Specification (WLC). Turn smartphones or other NFC-enabled devices into “portable charging stations.”

NFC charging technology, like Qi2, also uses electromagnetic induction technology. The WLC standard supports the use of an antenna in NFC devices to achieve two-in-one communication and charging functions, so currently only 1W charging speed can be achieved through this solution (WLC standard wireless charging supports 250 milliwatts, 500 milliwatts, 750 milliwatts and 1 watt four power transmission levels). This means that NFC-enabled devices can wirelessly charge IoT devices powered by small batteries without a cable.
Currently, the new WLC 2.0 defines a new antenna class next to the antenna class already defined by the WLC 1.0 specification. This new antenna category with a smaller antenna size allows for the implementation of micro-iot devices that can be charged by NFC technology, in addition to increasing the charging power to 3W.
(5) Ki
Wireless fast charge standard for kitchen appliances launched by WPC(Wireless Power Consortium, Chinese name “Wireless Charging Alliance”). Up to 2200 watts of power can be transmitted to smart wireless kitchen appliances, enabling them to operate without messy wires.

Making kitchen power both interoperable and secure, while giving designers and manufacturers plenty of design freedom to differentiate their products.
2.3 Charging standards for electric vehicles
(1) ChaoJi
ChaoJi is a complete conduction charging system solution including charging connection components, control and guidance circuits, communication protocols, charging system safety, thermal management, etc., which meets the requirements of fast, safe and compatible charging of electric vehicles. ChaoJi absorbs the advantages of the current four international DC charging interface systems, improves the insuperable defects of the original system, ADAPTS to large, medium and small power charging, and meets household and various public charging scenarios.
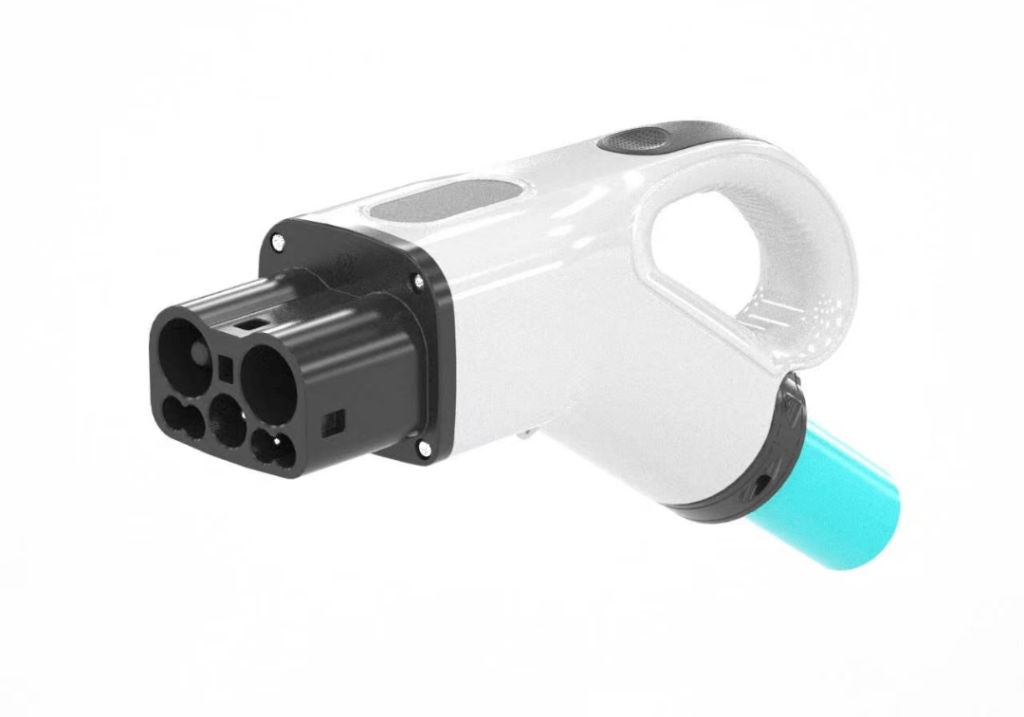

The interface structure is small and light, and it is fully optimized in mechanical safety, electrical safety, electric shock protection, fire protection and thermal safety design. It can be compatible with the existing four major international DC charging systems, and fully consider the needs of future industrial development, and can be upgraded smoothly. Compared with the existing interface systems, ChaoJi charging system has outstanding advantages in terms of forward and backward compatibility, enhanced charging safety, enhanced charging power, enhanced user experience and international recognition.
(2) CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO (Charge de Move) is a fast DC charging standard from Japan, jointly developed by the Japan Electric Vehicle Research Institute and Mitsubishi Electric to specify the charging interface between DC charging piles and electric vehicles.

The standard is now widely recognized internationally. Under the CHAdeMO standard, a special plug and connector are used between the charging pile and the electric vehicle for fast DC charging.
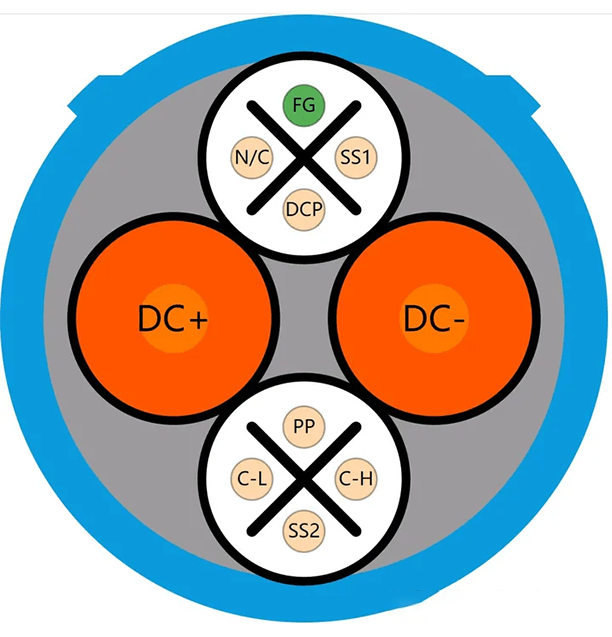
CHAdeMO is a DC plug jointly developed by five Japanese car manufacturers and tried to promote it as a global standard starting in 2010, but it has not been widely adopted. Despite this, there are many countries or regions that currently adopt the CHAdeMO interface, with the exception of Japan, most of which are installed in Europe (mostly in Northern Europe), the United States and South Korea. There are two versions of the CHAdeMO standard, the first version supports charging up to 62.5 kW and charging current up to 125 A; The revised CHAdeMO 2.0 specification allows up to 400 kW. At the same time, the CHAdeMO Association is also working with China to develop an ultra-fast connector capable of charging up to 900 kW, known as the chaoji charging interface, but progress has not been as expected.
(5) CCS
CCS (Combined Charging System) is an integrated charging system, CCS is the new energy vehicle charging standard used in Europe and the United States, and is divided into CCS1 and CCS2. The United States is CC1 and Europe is CCS2.
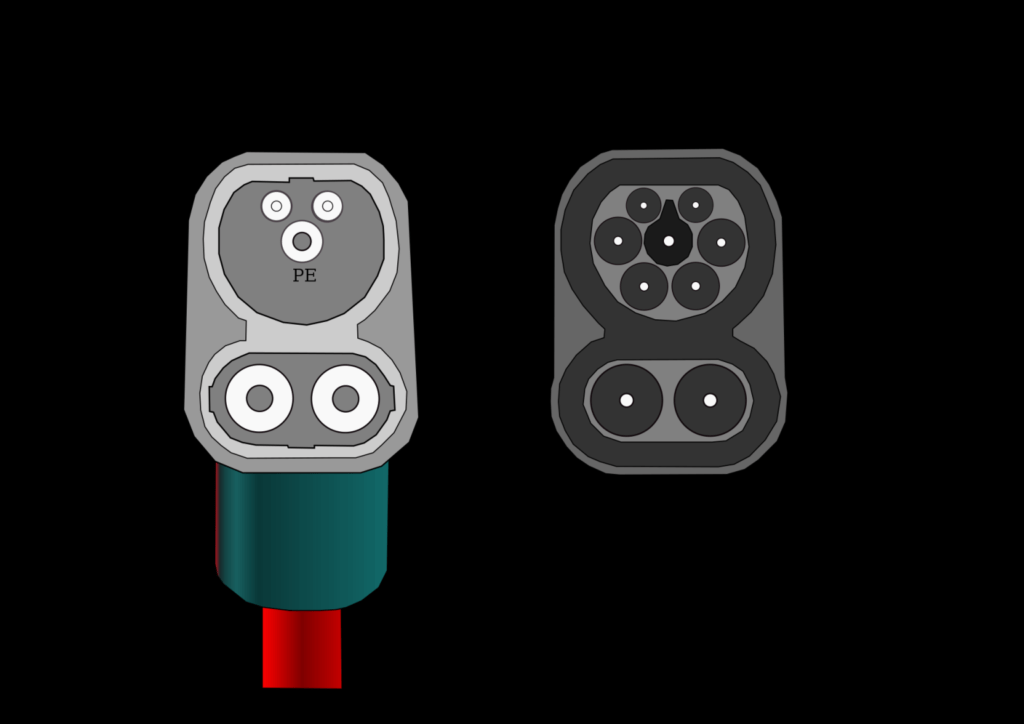
It combines Mennekes AC charging used in Europe with SAE J1772 DC charging standard used in the United States. It uses the same plug as the Mennekes Type 2 AC plug and adds two DC poles below it. In this way, CCS is compatible with AC charging and DC charging, which can meet the charging needs of different regions and different models.
(6) Tesla Supercharger
Tesla Supercharger is an electric vehicle charging standard developed by Tesla to specify the charging interface between Tesla electric vehicles and charging piles. Because Tesla has independently developed the entire electric vehicle ecosystem, its charging standards also have certain uniqueness.

This standard applies to Tesla’s electric vehicles, which can be quickly charged with high power at Tesla Supercharger stations. It is reported that Supercharger V4 rated voltage 1000V, rated current 615A, working temperature across -30℃ -50 ℃, support IP54 waterproof, the output power is limited to 350kW. That’s an increase of 1,400 miles per hour and 115 miles per 5 minutes, or about 190km.
As a comparison, the maximum charging power of Supercharger V3 supercharging stations distributed more in China is 250kW.
3. Safety regulation
3.1 International organization
(1) International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), founded in 1906, is the world’s oldest international electrotechnical standardization body, responsible for international standardization work in the field of electrical engineering and electronic engineering. Its standards cover a variety of fields, including electronics, electrical, power, communication technology, and more. The IEC has developed a number of standards on safety, performance and interoperability, covering charging devices and battery technology.

The IEC has 81 member countries (60 full members and 21 associate members), called IEC National Committees, and each country can only have one body as its member. Each member state is a member of the Board, which meets once a year, called the IEC Annual Meeting, in turn in each member state. The Executive Committee deals with matters assigned by the Council. The technical work of IEC is the responsibility of the Executive Committee (CA). In order to improve the efficiency of the work, the Executive Committee is divided into three groups, A, B, and C, respectively in different areas to deal with the coordination of standards development work. China became an executive board member of IEC in 1957.
(2) International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO), established in 1947, is an international organization in the field of standardization, the organization self-defined as a non-governmental organization, the official languages are English, French and Russian. ISO I comes from the Greek ISOS, meaning “equality”. ISO currently has 165 members, including national standards bodies and major industrial and service companies in member States.

The Standardization Administration of China (administered by the State Administration for Market Regulation) joined ISO in 1978, and at the 31st International Standards Organization General Assembly in October 2008, China officially became a permanent member of ISO. ISO is responsible for standardization activities in most fields in the world today (including military, petroleum, shipbuilding and other monopoly industries), and carries out technical activities through 2856 technical structures (including 611 technical committees, 2022 working groups, and 38 special working groups).
The object and purpose of the International Organization for Standardization is: “To promote standardization throughout the world in order to facilitate the international exchange of goods and services and to expand cooperation in the fields of knowledge, science, technology and economy.” Its main activities are to formulate international standards, coordinate worldwide standardization work, organize members and technical committees to exchange information, cooperate with other international organizations, and jointly study standardization issues.
(3) International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is an important specialized agency of the United Nations and the oldest international organization of the United Nations. Referred to as “International Telecommunication Union”, “ITU” or “ITU”. Itu is the United Nations agency responsible for the allocation and management of global radio spectrum and satellite orbit resources, the development of global telecommunications standards, the provision of telecommunications assistance to developing countries and the promotion of global telecommunications development.

As a link between governments and the private sector worldwide, ITU is the host of the World Summit on the Information Society through its radiocommunication, Standardization and Development Telecommunications exhibitions. Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, ITU’s membership comprises 193 member States and more than 700 sectoral and associate sectoral and academic members. World Telecommunication Day is celebrated on 17 May each year.
The purposes of the ITU, in accordance with its Basic Law, may be defined as follows: 1) To maintain and develop international cooperation to promote the research, development and rational use of all telecommunications services; (b) Promote the upgrading and most effective use of telecommunications facilities, improve the efficiency of telecommunications services, increase their utilization and achieve as much popularization and universalization as possible; 3, the coordination of national work, to achieve a common purpose, these work can be divided into telecommunications standardization, radio communication specifications and telecommunications development three parts, each part of the permanent functional departments are “bureaus”, including the Telecommunications Standards Bureau (TSB), Wireless Communications Bureau (RB) and Telecommunications Development Bureau (BDT).
3.2 Regional safety organizations
(1) American Safety Laboratory (UL)
UL (full name: UNDERWRITERS LABORATORIES INC.) is a non-profit safety certification organization focused on testing and certifying the safety of a variety of products, including electronic devices and charging devices. Founded in 1894, the company is headquartered in Northbrook, Illinois, with branches in Long Island, New York; Tampa, Florida; and Santa Clara, California.

UL Corporation is the most authoritative in the United States and the world’s largest private inspection organization for inspection, testing and identification of various electrical products. The laws of many states in the United States expressly stipulate that home appliances without the UL mark are not allowed to be sold on the market.
UL Engineering Inspection is organized into six divisions: Anti-theft and Signals, Disaster and Chemical Hazards, Electrical, Fire Protection, Heating, air conditioning and refrigeration, and Marine Supplies. UL provides safety performance audit, testing, and identification of building materials, fire prevention equipment, mechanical and electrical equipment, Marine equipment, oil and gas equipment, and follow-up testing and inspection during factory production according to UL standards, and affiils the UL mark.
(2) European Committee for Standardization (CEN)
Comite Europeen de Normalisation (French abbreviation: CEN) was founded in 1961 and is headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. It is a non-profit international standardization science and technology institution composed of national standardization institutions with Western European countries as the main body. One of the three major European standardization bodies.

The purpose of the CEN is to promote standardization collaboration among member states, to develop European standards (EN, except for the electrical industry) and harmonized documents (HD) needed in the region, and to form the Information Technology Steering Committee (ITSTC) together with CENELEC and ETSI, to develop functional standards for interconnected Open Systems (OSI) in the field of information.
(3) China National Standard (GB)
China’s national standards are formulated and issued by The State Council’s subordinate organ unit “National Standardization Administration”, which also includes the national standard code of the language coding system, “National Standardization Administration” is also the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (or the International Electrotechnical Association, IEC) on behalf of the People’s Republic of China member institutions. It is the unified standard of the People’s Republic of China, referred to as the “national standard”. “GB” is the code name of the national standard of the People’s Republic of China, taken from the Chinese pinyin initials of the “National Standard”.
The mandatory standard is labeled “GB”. The recommended standard is labeled “GB/T”. Compared with many ISO international standards, many national standards are identical to other standards (IDT, identical to other standards), modified in relation to other standards (MOD, modified in relation to other standards; Before 2000, it was called “equivalent adoption, EQV, equivalent to other standards” or “NEQ, not equivalent to other standards”.
(4) China Compulsory Certification (CCC)
The full name of CCC Certification is “China Compulsory Product Certification”, the English name is China Compulsory Certification, the English abbreviation CCC, so it is also referred to as “3C” certification. It is a product conformity assessment system implemented by the Chinese government to protect consumers’ personal safety and national security, strengthen product quality management, and comply with laws and regulations.
On December 3, 2001, China issued a compulsory product certification system, and since May 1, 2002, the CNCA has accepted the first batch of certification applications for 132 products in 19 categories included in the compulsory product catalog. It is a product conformity assessment system implemented by the Chinese government in accordance with relevant WTO agreements and international prevailing rules, in order to protect the personal safety of consumers, the life of animals and plants, the environment and national security.

The General Administration of Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China and the Certification and Accreditation Administration of the People’s Republic of China jointly issued the Provisions on the Administration of Compulsory Product Certification on December 3, 2001, implementing the compulsory certification administration of “unified catalogue, unified standards and assessment procedures, unified marks and unified fees” for 132 products in 19 categories listed in the catalogue. The original “CCIB” certification and “Great Wall CCEE certification” are unified into “China Compulsory certification”.
In July 2023, the General Administration of Market Supervision issued an announcement to implement CCC certification management for lithium-ion batteries and battery packs and mobile power supplies from August 1, 2023. Since August 1, 2024, without the CCC certification and marked certification mark, may not be factory, sale, import or use in other business activities.
(5) China Quality Certification Center (CQC)
CQC is the abbreviation of China Quality Certification Center, the English full name is “China Quality Certification Centre”. It is a third-party certification body authorized by the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, and is one of the certification bodies in China, responsible for verifying the safety and compliance of various products. In March 2007, in order to speed up the adaptation to the new situation of the local Chinese inspection and certification market opening to the outside world, the former AQSIQ restructured and reformed the former China Quality Certification Center (CQC) and the former China Inspection and Certification Group (CCIC) to make CQC and CCIC two brands better and stronger.

CQC has 45 branches at home and abroad. The service network all over the country can provide customers with timely, thoughtful and high quality service. It is the only national certification body (NCB) in the IECEE-CB system and a full member of IQNet. The international mutual recognition business between CQC and many well-known certification bodies abroad, as well as extensive international exchanges and a good international image, can enable customers to enjoy value-added services.
Its purpose is to promote the improvement of product quality, protect the rights and interests of consumers, and promote the sustainable development of enterprises through certification, inspection, testing and other services. The quality goal is to win the trust of customers with high quality and efficient working style and overall consistent working level; In the field of certification, always maintain the leading position in China; Among the ranks of internationally renowned certification bodies.
(6) Japan Electromagnetic Interference Control Committee (VCCI)
VCCI is a Japanese certification mark for electromagnetic compatibility and is administered by the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by Information Technology Equipment. Evaluate information technology products for VCCI compliance under CISPR 22.

VCCI certification is optional, but information technology products sold in Japan are generally required to undergo VCCI certification, which is used to test and confirm the electromagnetic compatibility and safety of electronic equipment.
Japan’s VCCI is a membership system, and the testing laboratory must be a VCCI member before the VCCI report can be issued. Businesses that use the VCCI logo must also become VCCI members. Enterprise products need to pass the VCCI certification, first send the product to the VCCI member laboratory for testing, after getting the test report, need to apply to the VCCI to become a member, after becoming a VCCI member, the product using the VCCI logo is legal.
(7) Australian Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (ACMA)
ACMA certification is a certification issued by the Australian Communications and Media Authority. ACMA certification is an important part of Australian telecommunications regulations and aims to ensure that telecommunications equipment meets relevant technical and safety requirements during use.
ACMA certification covers a range of telecommunications products, including radio transmitting equipment, communication cables, telephone equipment, satellite communication equipment, wireless local area network equipment, etc. Holding ACMA certification allows you to sell your products on the Australian market.
Summary
This article brings together a variety of technical standards in the field of fast charging, involving both wired and wireless charging of electronic devices, as well as the field of new energy vehicle charging. These mainstream fast charging technology standards have played an important role in regulating the development direction of the industry, and they can be the first time to understand the latest developments in fast charging technology.
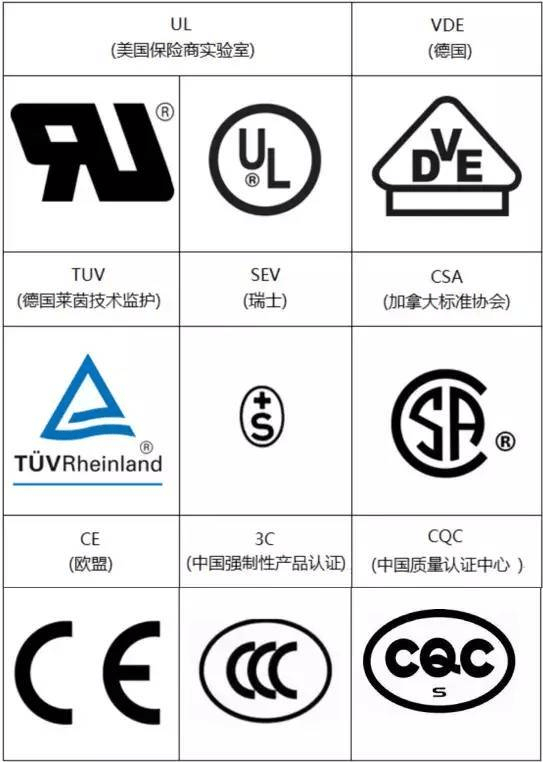
In addition, the safety regulations of various countries and regions are also important norms of the fast charging industry, technical specifications to ensure the development and unity of technology, and safety regulations to ensure the bottom line and safety of the industry. Here are some well-known safety regulations in countries and regions, but there are some omissions limited to space, such as: Germany’s TUV (Germany Rheinland Technical Guardian), Canada’s CSA (Canadian Standards Association) and so on.
All in all, different countries have their own safety regulations, although to a certain extent to ensure the quality and safety of the region, but also make the product circulation and technical exchange caused great obstacles. Therefore, it is still hoped that international organizations will complete the unification of norms as soon as possible on the basis of extensive exchanges, and the fast charging industry will usher in a new situation.
