How to test the temperature rise of a charger ?
Like ripple, conversion efficiency, and no-load power consumption, temperature is also an important parameter to measure the quality of a charger. Compared with ripple, conversion efficiency, and no-load power consumption, temperature should be the most directly perceptible to ordinary users. We can roughly judge the quality of a charger by relying on temperature.
1. How is temperature generated?
Speaking of temperature, we have to mention conversion efficiency. The charger converts the AC power in the socket into DC power and delivers it to the phone. However, the problem is that the charger cannot convert AC power into DC power completely (although we hope so, it is currently impossible). In the conversion process, some losses will occur, and the lost part will be manifested in the form of heat. This is the source of temperature when the charger is working.
2. Hardware required for testing
As mentioned earlier, among the various testing indicators of chargers, temperature is the most perceptible to ordinary users. Let’s take a look at what hardware is needed to test the temperature of a charger.
1) Thermostatic chamber

This is a thermostatic chamber. The literal meaning of thermostatic is constant temperature. Because the ambient temperature is different at different room temperatures, which means there are more variables for the charger.
2) Load tester
This is a load tester from Angnex. Its function is to allow the charger to output continuously and stably at a certain power, thus achieving the basis for testing the temperature of Power-Z.
3) POWER-Z tester

This is a POWER-Z tester, which needs no further introduction, mainly used to control the output voltage value of the charger.
4) Thermal imager

Finally, a thermal imager is also needed. Now, a basic environment for testing the temperature of the charger has been set up.
3. How to test the temperature of the charger

First, of course, place a 35W charger in the thermostatic chamber and connect it to the socket, and then use a C2C cable to connect it to the charger.

Connect the other end of the cable to the POWER-Z tester and induce the PD output gear. The testing principle is generally to test with the maximum output power of the charger when the PD fast charge is triggered. The chargers participating in the test support the maximum output power of 20V 1.75A 35W. Use the POWER-Z tester to induce the charger to output 20V. At this time, the voltage of the charger has been adjusted.

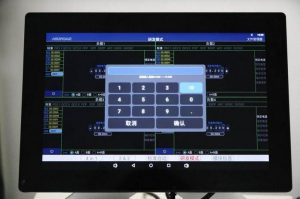
Then adjust the current to 1.75A on the operation panel of the tester.
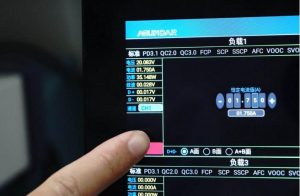
After adjusting, click on “start” and the load tester will continuously operate at a set power of 35W, while the charger will continuously output at a power of 35W.
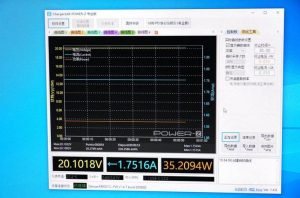
At the same time, the output power of the charger is monitored using the POWER-Z upper computer on the computer to determine whether the power has decreased during testing and to observe whether the output voltage is stable.
The time for the charger temperature test is set to 1 hour, during which the maximum output power when triggering PD fast charging of the charger is first determined, and then the maximum voltage output when the charger is outputting PD fast charging is induced using a POWER-Z tester. The charger is loaded to achieve maximum output power.

Then it is time to take out the thermal imager shown above, which is the tool needed for the final temperature data collection.

At this point, the thermal imager screen can already display the temperature on the surface of the charger casing. After taking the picture, the thermal imager will save the image to the internal storage of the machine. With that, the temperature test and final data collection for the charger is completed.
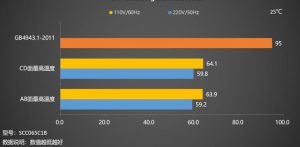
Finally, the temperature data of the charger will be presented in the form of a bar graph and compared with the standard set by GB4943.1-2011 to show the temperature control performance of the charger to the user, the lower,the better.
To summarize, the above is the process of the temperature test for chargers.
First, the maximum PD output power supported by the charger is checked,
and then the charger is placed in a constant temperature box at 25°C and loaded at maximum PD charging power for 1 hour.
Finally, the temperature on the surface of the charger is photographed using a thermal imager.
The temperature of a charger can be roughly judged by touching it, but the use of a thermal imager is necessary to determine the exact temperature.
