Long Distance Wireless Charging
With the popularity of wireless charging in mobile phones, its convenient features have gradually become ingrained in people’s minds.
In recent years, wireless charging technology has expanded beyond low-power applications in consumer electronics and has found broader application demands in the medium-power segment. Areas such as electric bicycles, inspection AGVs, and mobile robots have become huge potential markets for medium-power wireless charging.
However, wireless charging technology has long been constrained by technical bottlenecks such as “charging efficiency” and “foreign object detection,” which has made it uncommon in the market.
Recently, Tsee Technology officially released the TE03 wireless charging module for the 200W medium-power market. This article will provide a detailed “decrypting” of this latest medium-power wireless charging module.
1. See the product's detail
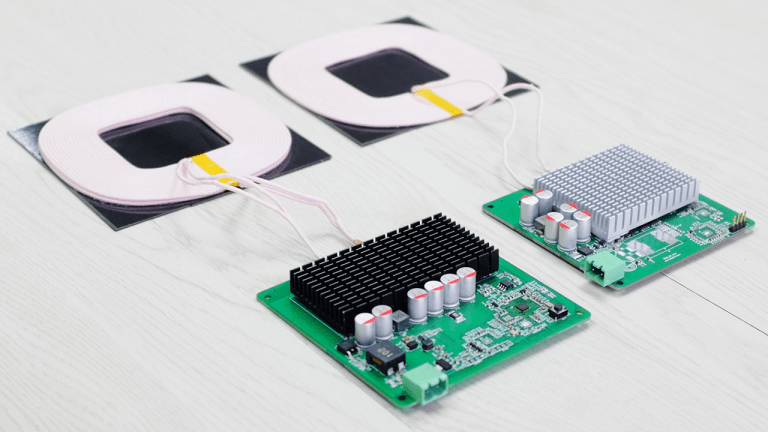
This 200W wireless charging module consists of a transmitter (Tx, left) and a receiver (Rx, right), both of which use green PCB boards and are equipped with north and south bridge heat sinks.
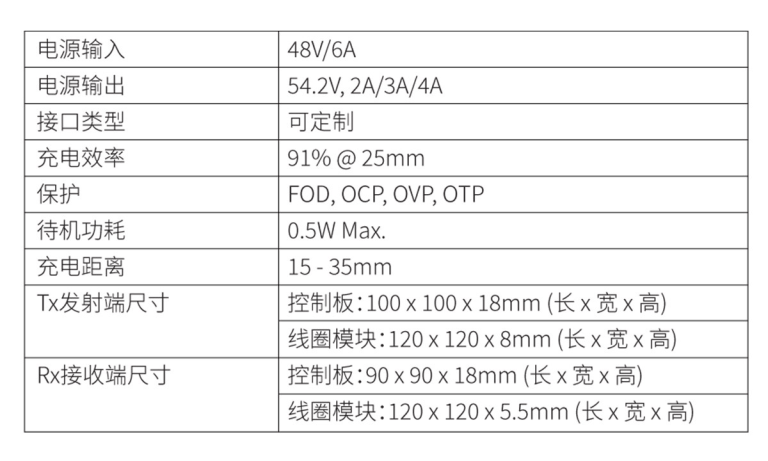
For the dimensions, the transmitter PCB measures 100*100*18mm, with a coil size of 120*120*8mm.
The receiver PCB measures 90*90*18mm, with a receiving coil size of 120*120*5.5mm.
The transmitter adopts 48V 6A input, while the receiver has a fixed 54.2V output and adjustable current options of 2A/3A/4A, with a maximum power output of 200.
Both power interfaces of this solution’s PCB boards can be customized, and they support various protection functions such as FOD (Foreign Object Detection), OCP (Overcurrent Protection), OVP (Overvoltage Protection), and OTP (Overtemperature Protection). The charging distance ranges from 15mm to 35mm, and the efficiency can reach up to 91% (at 25mm).
2. Performance Testing
2.1 Charging Efficiency Testing
First, the efficiency of the 200W wireless charging module was tested. In an ambient temperature of 24.8°C, an ADEX IT6722A DC power supply was used for power input, and an ADEX IT8512A served as the electronic load.
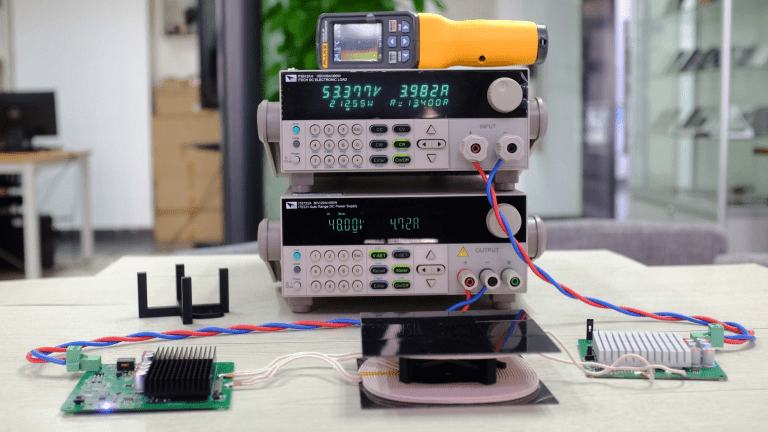
The graph above shows the scenario with a 20mm distance between the
transmitter coil and receiver coil, with an output current of 4A. The
test data indicates that with a DC power supply voltage of 48V and a
current of 4.72A, the electronic load voltage is 53.377V, and the
current is 3.982A, resulting in an efficiency of 93%.
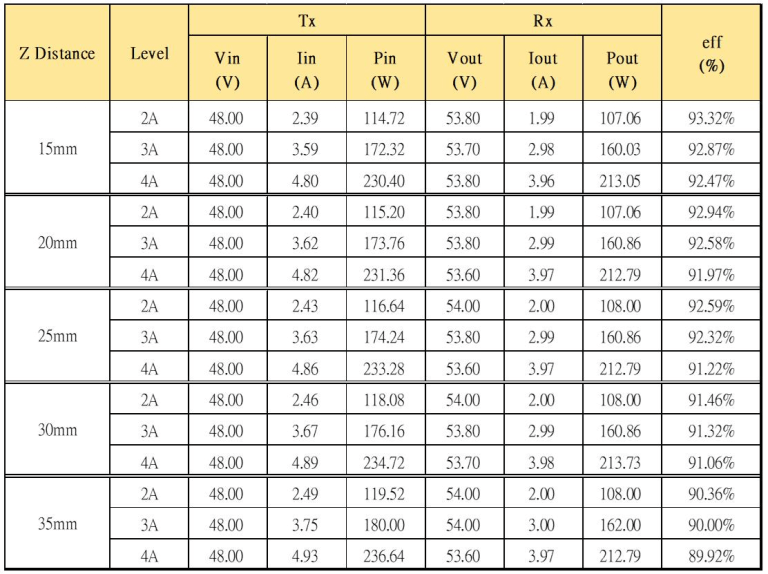
The efficiency data in different charging distances and output currents are shown above.
For distances between 15mm and 20mm, the system efficiency can reach approximately 92%. For distances between 25mm and 30mm, the efficiency remains above 91%. Even with a coil distance of 35mm, the system efficiency can still reach around 90%.
Transmission efficiency is one of the parameters that determine the quality of wireless charging. Based on the test data, the transmission efficiency of this 200W wireless charging module consistently exceeds 90%, demonstrating its excellent performance.
2.2 Offset Testing
Furthermore, tests were conducted to evaluate the influence of coil offset at different charging distances and different output currents on transmission efficiency.
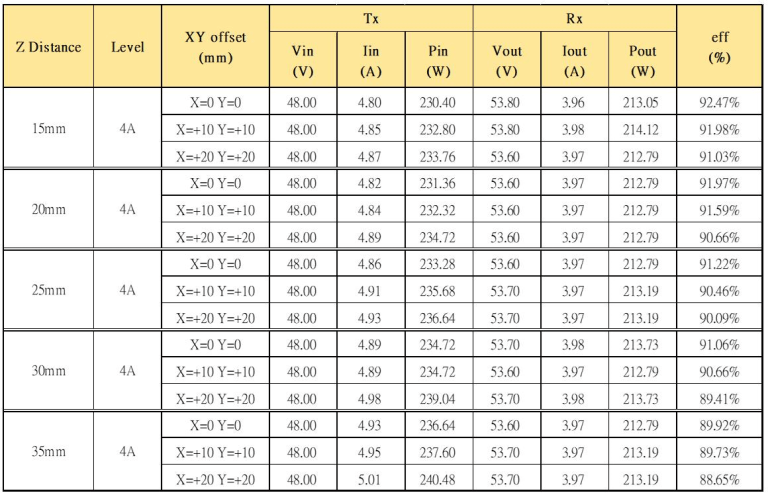
The table above shows the test data for coil distances ranging from 15mm to 35mm with offsets of 10mm and 20mm.
The results are highly satisfactory, as transmission efficiency can reach 90% within a charging distance of 30mm and an offset of 20mm. This fully demonstrates the advantages of wireless charging, allowing for convenient and perfect charging without the need for precise alignment.
2.3 Foreign Object Detection (FOD) Testing
In wireless charging, the presence of metallic foreign objects in the charging area can pose potential risks, such as heating caused by eddy currents in the metal, which can damage devices or even cause fires.
Foreign Object Detection (FOD) is primarily designed to prevent metal objects from heating up in the magnetic field and causing safety accidents. The 200W wireless charging module underwent testing for both power-on FOD and working FOD.
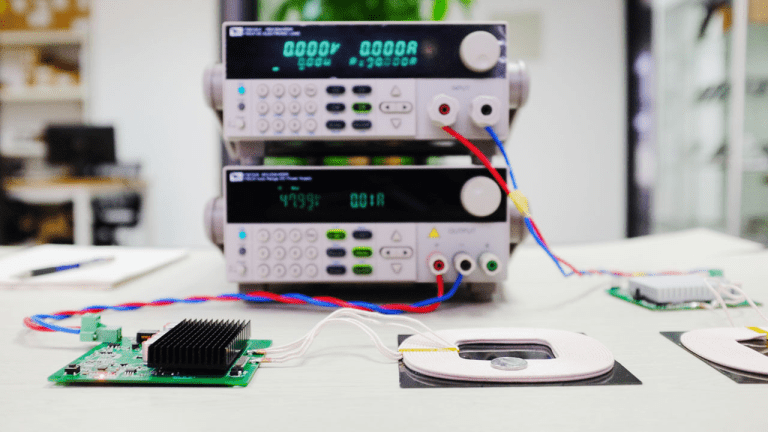
First, a “one-penny coin” was placed on the wireless charging transmitter coil. As seen from the DC power supply, there was no current output, indicating that the transmitter supports metal object detection in power-on mode. This feature effectively prevents the wireless charging coil from heating external metals in practical applications.
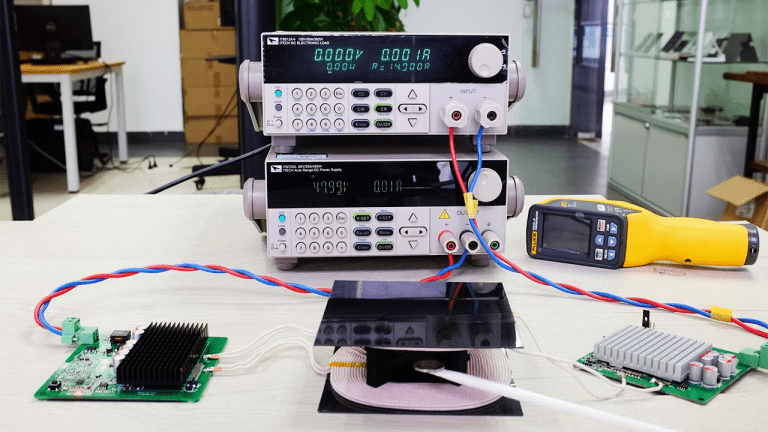
In addition to FOD detection in standby mode, the wireless charging system was also tested for FOD detection during operation.
The transmitter and receiver coils were positioned 35mm apart, and a DC power supply and electronic load were connected to put the system in normal operation. Then, a “one-penny coin” was placed between the two coils, and it was observed that the entire wireless charging system stopped power transmission. This indicates that the system detected the metal foreign object and triggered the FOD detection function.
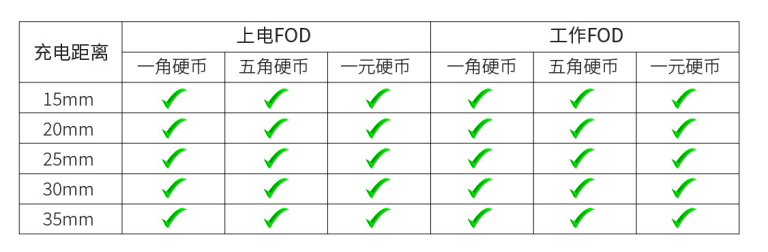
The FOD test was also conducted at coil distances of 15mm, 20mm, 25mm, 30mm, and 35mm in both power-on mode and working mode. The test results show that the system can accurately identify metal foreign objects and automatically stop charging, ensuring safety during practical usage.
FOD is one of the protection mechanisms in wireless charging, and excellent FOD performance enhances the safety of wireless charging. According to reports, Tsee Technology’s R&D team has made multiple improvements to the FOD algorithm for this wireless charging solution, achieving precise FOD functionality.
2.4 Temperature Rise Testing
Temperature rise testing was conducted with an ambient temperature of 24.9°C, a charging distance of 20mm, and an aging period of 1 hour at an output power of 200W. The FLUKE VT04A infrared thermal imager was used to measure and record the temperature rise.
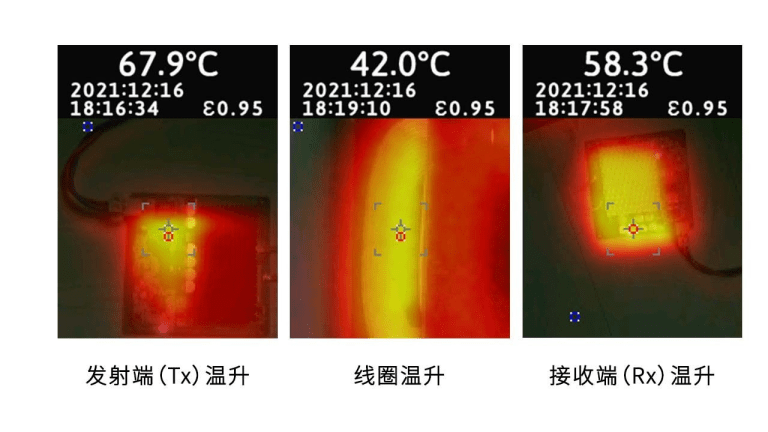
The test results show that the highest temperature reached approximately 67.9°C on the transmitter (Tx) side, around 42°C on the coil, and approximately 58.3°C on the receiver (Rx) side.
Furthermore, the temperature rise was tested with a charging distance of 35mm and an output power of 200W at an ambient temperature of 24.9°C.
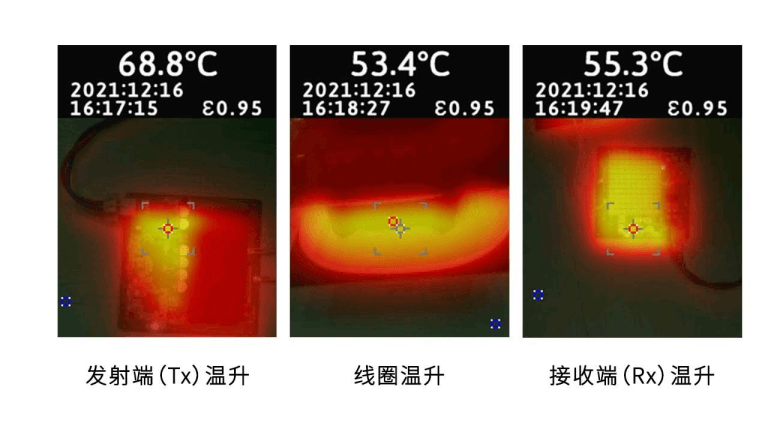
The test results show that the highest temperature reached approximately 68.8°C on the transmitter (Tx) side, around 53.4°C on the coil, and approximately 55.3°C on the receiver (Rx) side.
The two tested parameters, temperature rise during actual usage and sensitivity to foreign object detection (FOD), are fundamental to the application of wireless charging technology.
Based on the test results, it is evident that the 200W wireless charging module by Tsee Technology achieves excellent temperature rise control.
Coupled with sensitive foreign object detection, it can operate stably for a long time without any issues. Additionally, it features the advantage of charging without the need for precise alignment, making it more user-friendly. These achievements are the result of the strong R&D team of Tsee Technology and the collaborative efforts of its partners.
3. Conclusion
Wireless charging offers many unparalleled advantages compared to traditional wired charging, such as contactless charging, no plugging or unplugging, no electric sparks, and eliminating the risk of electrical leakage. It has no contact points, making it suitable for high-durability requirements in outdoor and high humidity environments. It boasts high reliability with no need for maintenance, no contact oxidation, and no risk of charging being affected by dirt or contamination. It allows for instant charging, providing a worry-free operation and ensuring that devices are always fully charged.
Since wireless charging has so many advantages, why is it rarely seen effectively applied in daily life? There are two main reasons: on one hand, solution providers often rush to release semi-mature solutions that do not meet market expectations, leading to a crisis of trust; on the other hand, the market needs more time to learn and prepare for widespread applications in the future.
Prior to the official release of the 200W wireless charging module, Tsee Technology has been investing in research and development in the field of medium-power wireless charging for many years. It maintains strategic partnerships with leading companies in various industries, continuously optimizing system efficiency, transmission distance, stability, and carefully refining system control, foreign object detection, and other algorithms. Not only does it achieve leading transmission efficiency in the industry, but also ensures stability and safety in practical usage through the development of relevant software functionalities.
To meet the diverse application needs, the Tsee Technology 200W wireless charging module can be customized to provide different output voltages, such as 36V, 24V, 19V, in addition to its current focus on charging for 48V batteries. This makes it suitable for a wider range of medium-power products. It is precisely because of Tsee Technology’s meticulous attention to every detail and cross-disciplinary collaborative innovation that we have today’s deployable and industrialized medium-power wireless charging products.
In the foreseeable future, medium-power wireless charging and power supply solutions will be widely applied in various fields such as mobile robots, electric bicycles, and mobile medical devices.
